Data acquisition is your best bet if you're looking to make informed decisions in today's information-driven world. But what exactly is data acquisition?
In simpler terms, it's the process of gathering and converting real-world observations or measurements into digital data that can be analyzed by computers.
Imagine it as the bridge between the physical world and the world of computers, allowing us to translate things we can sense (temperature, pressure, customer clicks) into a format that can be crunched, analyzed, and ultimately understood. This understanding is what empowers us to make truly informed decisions.
This article will be your beginner-friendly guide to the basics of data acquisition. Let’s get started!
Outline
What is Data Acquisition
What is a Data acquisition system?
Components of a Data Acquisition System
Importance of Data Acquisition
Selection Criteria for Data Acquisition
What is Data Acquisition?
Data acquisition, often abbreviated as DAQ, is the fundamental process of collecting and converting physical measurements into digital data that computers can understand. It's essentially the first step in transforming real-world observations, like temperature readings or machine vibrations, into usable information for analysis.
What is a Data Acquisition System?
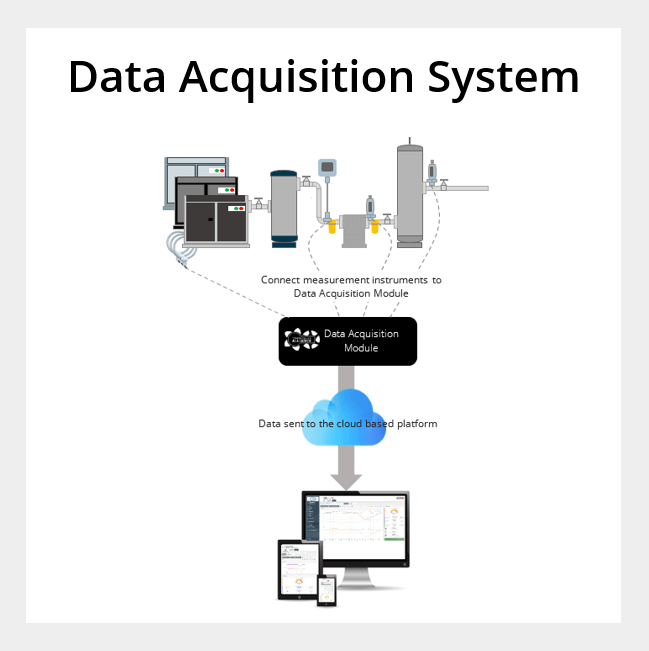
A data acquisition system is a comprehensive setup that comprises of measurement instruments, sensors, a computing unit, and specialized software designed for capturing, storing, visualizing, and analyzing data. It serves the purpose of gathering essential information to comprehend various electrical or physical phenomena.
Data acquisition systems come in diverse forms, ranging from handheld devices for basic temperature measurements to extensive systems encompassing numerous channels, often installed across multiple racks and operated remotely.
In simple terms, DAQ is a a three-part system designed to capture real-world measurements and translate them into a format computers can understand.
Components of a Data Acquisition System
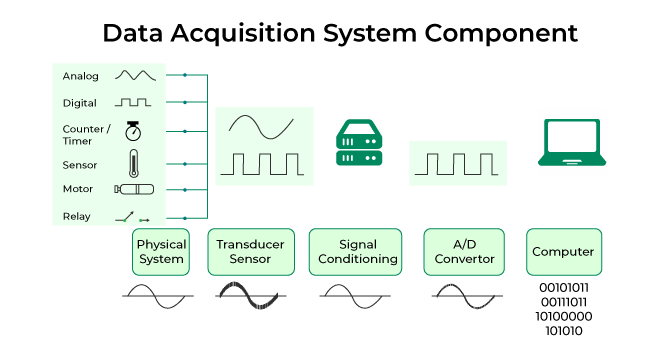
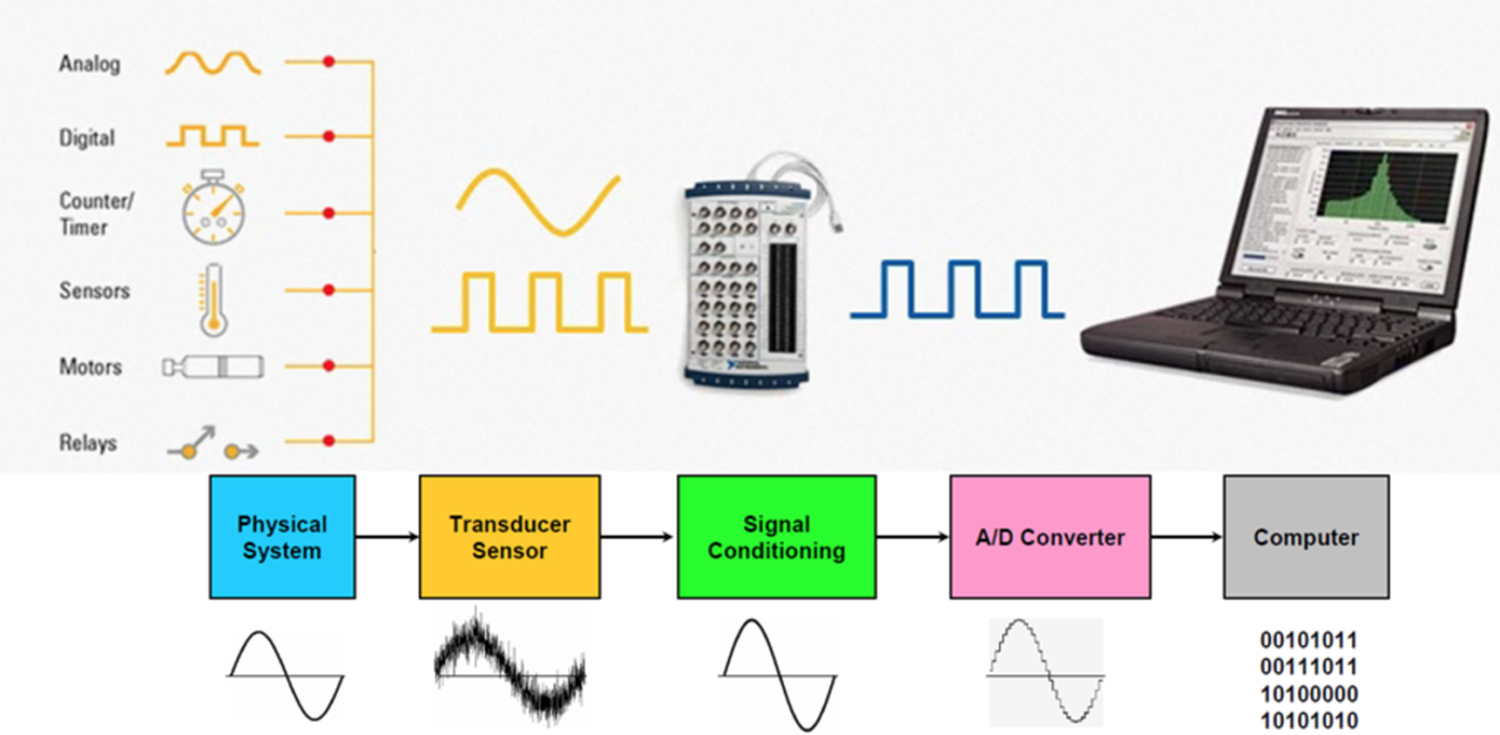
A Data Acquisition System includes three essential components known as sensor, single conditioner, and the Analog to digital converter.
Firstly, the sensor, also known as a transducer, converts real-world conditions like temperature or motion into electrical signals. These signals serve as the input for the DAQ system.
Next, the signal conditioner refines the raw analog signals from the sensor. It can amplify, attenuate, filter, calibrate, or isolate the signal. This process is crucial as real-world data can be noisy or potentially hazardous without proper filtering.
Finally, the Analog to digital converter converts the refined analog signal into digital information. This digital data becomes interpretable by a computer or processor. Subsequently, the information is
Benefits of Data Acquistion
Data acquisition offers several key benefits across industries. Firstly, it enables organizations to gain valuable insights into complex systems and processes by capturing essential information about electrical or physical phenomena. This data serves as a foundation for informed decision-making, facilitating improvements in efficiency, reliability, and safety across diverse applications.
For instance, by acquiring data from sensors, measurement devices, and other sources, companies can gain valuable insights into processes, performance, and trends, facilitating informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Secondly, data acquisition supports regulatory compliance by ensuring the accurate capture and documentation of critical information, thereby mitigating risks and safeguarding against potential liabilities.
Overall, the benefits of data acquisition lie in its ability to empower organizations with timely and actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making, operational efficiency, and regulatory compliance.
Importance of Data Acquisition Systems
1. Efficiency and Reliability Enhancement: Data acquisition systems play a crucial role in improving the efficiency and reliability of processes or machinery across various industries. It does this silently monitoring parameters such as machinery conditions or energy consumption, which in turn enable these systems contribute to optimizing operations and ensuring safety.
2. Enhanced Data Accessibility and Security: DAQ systems provide easier access to data for users, enhancing data security by minimizing human involvement in data capture processes and reducing associated risks.
3. Reduction of Data Redundancy and Errors: Implementation of data acquisition systems reduces data redundancy and minimizes errors by automating data entry processes, thereby enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
4. Cost Reduction in Data Management: Data entry, storage, and retrieval costs are significantly reduced with the adoption of data acquisition systems, as they facilitate faster data entry, efficient space utilization, and quicker retrieval.
5. Real-time Monitoring and Intervention: With real-time data acquisition capabilities, technicians can promptly identify and address issues, leading to faster problem resolution and optimal machine performance.
6. Quality Control and Product Testing: Data acquisition systems contribute to quality control by confirming whether systems meet design specifications and products meet user requirements. They also enable product testing for quality assurance and defect detection.
7. Automated Process Supervision: These systems enable the automated supervision of various procedures, allowing for swift fault detection and resolution without requiring constant human interaction.
8. Integration and Reliability: Data acquisition systems facilitate improved data integration and reliance on fewer programs, streamlining processes and ensuring completeness and correctness of information.
Selection Criteria for Data Acquisition
When selecting data acquisition systems, specific criteria guide the decision-making process to ensure optimal performance and alignment with project objectives. Here's a breakdown of key selection criteria for data acquisition systems:
1. Measurement Accuracy: The system should offer precise measurement capabilities, and must be able to minimize errors and ensure the fidelity of collected data.
2. Sampling Rate and Resolution: Consider the system's ability to capture data at the required frequency and resolution to meet project requirements without sacrificing accuracy.
3. Signal Conditioning: Evaluate the system's built-in signal conditioning features, such as amplification, filtering, and isolation, to enhance the quality of acquired signals and mitigate interference.
4. Sensor Compatibility: Ensure the DAQ system has compatibility with a wide range of sensors and transducers to accommodate diverse measurement needs across various applications.
5. Scalability: Choose a system that can scale up to handle increasing data volumes or additional channels as project requirements evolve over time.
6. Data Transmission: Assess the methods used for data transmission, including wired (e.g., Ethernet, USB) or wireless (e.g., Wi-Fi, Bluetooth) connectivity options, to facilitate seamless data transfer to processing or storage platforms.
7. Integration with Software Tools: Verify compatibility with software tools for data visualization, analysis, and storage, ensure there is smooth integration into existing workflows and systems.
8. Real-time Monitoring and Control: Consider whether the system supports real-time monitoring, control capabilities, and allows users to react promptly to changes or anomalies in acquired data.
9. Robustness and Reliability: Choose a system with durable construction and reliable performance, capable of operating consistently in challenging environments or industrial settings.
10. Cost-effectiveness: Balance the features and capabilities of the system with the overall cost, including initial investment, maintenance, and long-term operational expenses, to ensure optimal value for the organization.
11. Support and Maintenance: Evaluate the availability of technical support, documentation, and maintenance services from the system manufacturer or vendor to address potential issues and ensure ongoing system performance.
Types of Data Acquisition Systems
1. Handheld data acquisition systems: are portable devices designed for convenient data collection in various settings. These devices are typically compact and easy to use, making them suitable for fieldwork or applications where mobility is essential. They often come equipped with basic sensors and interfaces for quick measurements and data logging.
2. Portable data acquisition systems: offer more advanced features compared to handheld devices. They include a built-in computer, storage, and display, providing greater versatility and functionality for on-the-go data acquisition tasks. These systems are also commonly used in research, engineering, and industrial applications where mobility and real-time data processing are critical.
3. Modular data acquisition systems: consist of separate modules or components that can be customized and interconnected to create a tailored data acquisition solution. These systems offer flexibility in configuration, allowing users to select modules for signal conditioning, data acquisition, processing, and communication based on their specific requirements.
Furthermore, modular systems are suitable for applications with varying measurement needs or environments where scalability and adaptability are essential.
4. Rack-mountable data acquisition systems: are designed to be installed in standard equipment racks or enclosures. These systems are space-saving and organized, making them suitable for installations in control rooms, laboratories, or industrial settings where multiple instruments need to be housed together.
Conclusion
Data acquisition encompasses the systematic process of gathering, storing, and analyzing data from various sources, ranging from sensors and instruments to digital systems. It enables organizations to capture valuable information about physical or electrical phenomena, facilitating informed decision-making, process optimization, and innovation.
Related post
Recent Posts
Need help with a project?
© Wazobia Technologies 2025
Powered by: